Search knowledge database/FAQ
This page displays the KB (Knowledge Base) and/or FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) information that we have developed, and allows you to enter a word/s, or a phrase that is indicative of the question that you want to ask, to determine whether information about your topic is already held in our database. The Knowledge base is a collection of questions and answers that we believe provide quality information about a range of topics that our client base is interested in. The FAQ is a subset of the KB that addresses commonly asked questions.
Reviewing this page and/or performing this search before you submit your question may save you time by obtaining a result immediately, rather than waiting on a result from our service.
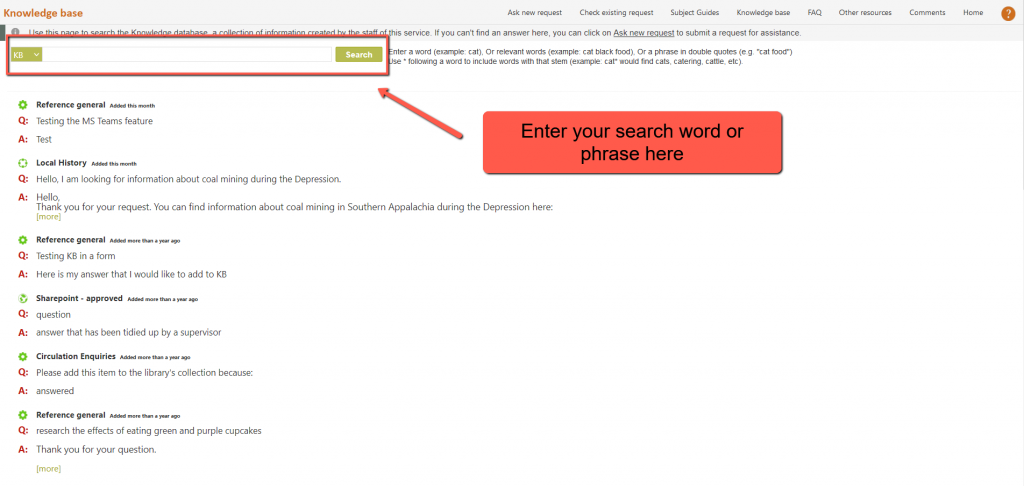
The coloured button to the left of the search box will show you the type of entry that is showing in the page and will be searched, and if we have both KB and FAQ entries for you to browse and search, you will be able to choose between the two types of entry using that button. The FAQ is a subset of the KB and so searching the KB ALSO searches the FAQ. Searching the FAQ limits your search to just the FAQ items.
On initial display this screen shows a Search box and the most recently added items to the KB or FAQ, ready for you to browse.
Search strategies to help you narrow your search
Oftentimes, your search will produce results that aren’t relevant to what you want to find out. Use these strategies to help narrow your search and pinpoint the results to fit your needs.
Searching for a word
Say you are on holiday and looking for local places to catch catfish. You could search for catfish or perhaps fishing, and the system will find occurrences of those exact words. However the information that you want may simply be referred to as “fish” and the use of wildcards (*), for example, a word stem search for fish*, will allow you to find a wider range of occurrences e.g. fish, fishing, and fisherman.
The wildcard *
Wildcard searching, or placing an asterisk (*) provides accuracy and flexibility in searching as shown by the following examples:
– A search for cat will find the exact word cat, but not cathode
– A search for *at will find any word ending in “at” e.g. cat and pleat
– A search for at* will find any word beginning with “at” e.g. ate and attend. Use this type of search for word stem searching e.g. fish* will find fish, fishing, fisherman, etc.
– A search for *at* will find any word containing the adjacent letters “at” e.g. operation, pattern, attend
– A search for a*t will find any word beginning with “a” and ending in “t” regardless of the word’s length e.g. attempt and abstract.
– A search for a, or any other single character or number, will result in a request for further information as individual characters or numbers are insufficient information to perform a search.
– A search for * will find ALL words, and therefore all questions and answers, in this database.
Searching for a phrase
If you enter several words surrounded by double quotes we will treats it as a phrase. For example, if you search for “black cats”, we will find questions and answers that include the two words black cats occurring together and in that order. It will not find questions and answers that includes phrases like cats that are black, because, although the same words occur, they do not occur in the same order and juxtaposition i.e. they do not occur as the exact phrase “black cats”.
If you enter more than one word we treat it as a phrase. For example, if you search for black cats i.e. without any double quotes around it, we will find questions and answers that include the both of the individual words black and cat in them. This is called a Boolean AND search because both black AND cat must appear.
Searching for hyphenated or compound words
Compound words are words made from multiple words.
For example the word database is composed of data and base and can legitimately be written as database, data-base, or data base.
When searching for compound words you should always search for the hyphenated form.
For example, searching for data-base will find all variants – database, data-base and data base.
Whereas, searching for database will only find database, and searching for data base will only find data base and data-base.
Starting the search
When you have entered the word/s you want to search on, including any wildcards, click on the Search button to see the relevance ranked results.